[ad_1]
Making a project-based learning (PBL) endeavor with youthful learners can seem daunting at first, and loads of questions may come up. How can teachers take into account whether or not or not the problem genuinely shows the concepts of PBL? What necessary elements should teachers persistently assess to ensure alignment with the PBL technique? And the way in which can they efficiently measure the success of their implementation?
The checklists beneath can perform helpful devices for answering these and completely different questions and for celebrating the successes in implementing PBL.
Readability of Problem Aims for Learners
Has the problem been pushed by the pursuits of the learners, and do faculty college students understand the goal and significance of the problem? Is the aim associated and important to their experiences, and is it clearly outlined and efficiently communicated?
When teachers and learners define the goals of a PBL problem, the principle focus have to be on contributing positively to the group, discovering perform, discovering choices to points, or exploring varied approaches.
The aim of the problem for the learners is simply not strictly tied to the curriculum nevertheless should naturally unfold to embody quite a few issues, areas, and talents that align with it. Empower learners to take the lead by deciding on issues that curiosity them and provide a broad context for content material materials acquisition and talent progress.
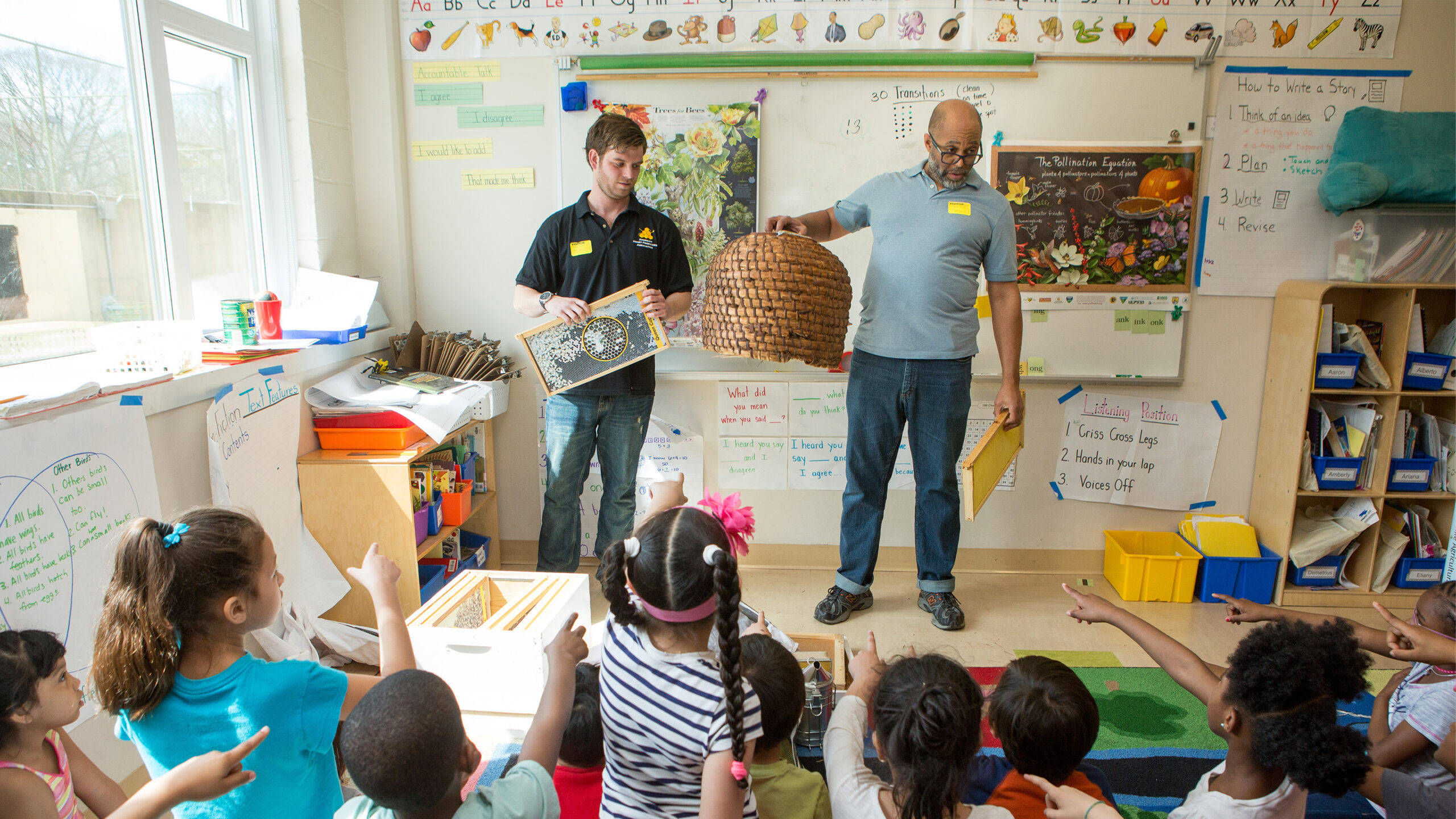
Adopting this nonlinear technique permits the blending of the emergent learning factors all through the PBL course of. As an example, in a first-grade classroom, faculty college students might categorical their curiosity about bees with the question, “Why don’t bees make a beehive in our school?” This question can perform the inspiration for the problem’s Driving Question. From there, teachers can data learners to find the circumstances very important for bees to assemble their hives.
This inquiry opens up a wealth of issues from the curriculum, allowing for exploration of themes related to the ambiance—bugs, local weather, and seasons, for example. All by means of their evaluation, faculty college students will work together with concepts from quite a few subjects, along with math, language arts, geography, social analysis, and further, whereas the principle focus stays on the problem as a result of the central intention.
The Central Question
Does the problem cope with a central question that’s very important and associated to the students? Does the question or draw back encourage investigation and creative choices?
The Central Question, developed collaboratively with learners, focuses on what they should uncover or create related to their chosen topic. For example, developing on their curiosity in bees and the question of why there are no beehives in school, the coach and faculty college students might formulate a Central Question paying homage to “How can first-grade faculty college students on the school create the circumstances for bees to assemble a hive in our playground?” The additional specific the Central Question, the upper, as a result of it guides the problem’s path and retains the inquiry centered.
The relevance of students’ autonomy
Do faculty college students have the prospect to make needed decisions regarding the problem? Does the problem allow faculty college students to work independently and deal with duties?
Current alternate options for important decision-making all through the problem. This may increasingly include asking learners to resolve on the specifics of what they should uncover or the methods they want to use.
For example, with the problem on bees and beehives, faculty college students might decide whether or not or not they should evaluation the development of a hive, the group of bees contained within the hive, completely different types of bees, or the acceptable local weather circumstances for specific bees. They may moreover choose straightforward strategies to present their findings—by means of drawings, exhibits, or maybe a category effectivity.
Encouraging these choices not solely fosters faculty college students’ sense of possession however as well as helps develop teamwork and collaboration skills, necessary pondering, and problem-solving skills. Daily teachers will uncover that the youngsters can cope with further independence and accountability of their initiatives as they flip into assured with the technique. In consequence, teachers can design duties that allow learners to work on their very personal or in small groups.
As an example, with a problem centered on bees and beehives, faculty college students might look at the wind energy in quite a few areas of the playground. They may take turns serving as “wind controllers,” each accountable for specific duties paying homage to measuring wind velocity, recording observations, and updating a chart to doc their findings.
This hands-on involvement not solely boosts their confidence however as well as fosters a method of accountability and empowers youngsters to take price of their learning whereas creating necessary life skills.
Precise-World Connection
Does the problem have clear connections to the true world? Is it related to real points that faculty college students might encounter exterior the classroom?
Establishing connections to the true world is crucial for making learning associated and fascinating. When a problem ties into real-life situations, it helps learners see the wise software program of their analysis. For example, inside the bees problem, faculty college students can uncover how bees contribute to the ecosystem and the importance of pollination in meals manufacturing. They may even go to a neighborhood yard or apiary, letting them watch bees in movement and understand their place inside the ambiance.
By tackling these real-world challenges, they be taught to suppose critically and collaboratively, brainstorming choices that might have a tangible have an effect on on their group. Such experiences deepen their understanding and enhance their enthusiasm for learning.
The reflection course of and recommendations
Are there alternate options for faculty youngsters to copy on what they’re learning and the problem course of? Are self-assessment and peer recommendations impressed?
Alternate options for reflection are important for deepening faculty college students’ understanding and fostering a improvement mindset. Widespread reflection lessons allow faculty college students to critically assess their experiences and set up areas for enchancment.
For example, after a bit of the beehive problem, faculty college students can accumulate in small groups to debate what went properly and the challenges they encountered, asking questions like “What shocked you about bees?” or “How has your view on their significance modified?”
Encouraging self-assessment and peer recommendations moreover promotes collaboration and regular enchancment. After presenting their findings on beehives, faculty college students can work together in structured recommendations lessons using a straightforward rubric to guage factors like readability and creativity. This course of helps them be taught to current and acquire constructive recommendations and take possession of their learning.
Preserving a journal for self-reflection extra fosters accountability and personal goal-setting. By integrating reflection and recommendations, teachers create a supportive ambiance that empowers faculty college students to develop and collaborate efficiently.
Solutions permits the coach to develop an movement plan to strengthen any weak areas and maximize the have an effect on of PBL on faculty college students. Utilizing the recommendations, teachers can set up developments or widespread challenges confronted by faculty college students.
For example, if quite a few faculty college students battle to know the place of pollination, the coach might decide to revisit this concept with further hands-on actions or seen aids, paying homage to motion pictures or diagrams illustrating how bees pollinate flowers.
Closing Product and Analysis
Have the learners designed a tangible remaining product or presentation? Is that this product important for the learners and does it reveal the academic and talents acquired?
Ensure that the final word product or presentation embodies creativity, relevance, collaboration, and talent demonstration. Throughout the above examples involving bees, the final word product is also a model of a bee habitat accompanied by a presentation that highlights key learnings.
The elements of the final word product may embody the bee habitat model and the way in which its creation involved group collaboration, the evaluation achieved, an oral presentation event with an viewers, and recommendations and reflection.
This remaining product—a collaborative bee habitat model and fascinating presentation—offers a tangible last end result that demonstrates the learners’ understanding of the place of bees in our ecosystem. It permits for creativity, teamwork, and the equipment of newly acquired data in a major method. By sharing their work with the group, faculty college students not solely have time their learning however as well as elevate consciousness regarding the significance of bees and conservation efforts.
As you embark on this thrilling PBL journey, don’t forget that the tactic is as helpful as the final word product. Each question explored, each capability developed, and each collaborative second contributes to a richer, further partaking tutorial experience. Have enjoyable the small victories, encourage reflection, and always adapt your technique based on recommendations and insights.
[ad_2]
Provide hyperlink